Discover what a good AMH level is for achieving pregnancy. Learn about the importance of AMH levels, fertility factors, and expert advice for increasing your chances of conceiving. Now is the time to get detailed information!
Understanding your reproductive health is essential when trying to conceive. The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) level is an important consideration. An essential component of determining ovarian reserve and fertility potential is the hormone AMH, which is produced by the ovaries. This extensive manual will delve into the subject of “What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant?” and offer professional advice, reliable data, and practical advice to help you increase your chances of becoming pregnant.
Table of Contents
What is AMH?
The growth and operation of the reproductive system are significantly influenced by the glycoprotein hormone known as the anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH). It is made by granulosa cells in ovarian follicles and aids in controlling the development and maturation of eggs inside the ovaries. To determine a woman’s ovarian reserve—the number of viable eggs still present in her ovaries—AMH is frequently used as a biomarker. The hormone is present in females from birth and levels usually start to drop significantly as menopause approaches in women. Let’s talk more about what AMH is optimal for conception.
What is an AMH test?
The level of Anti-Müllerian Hormone in the blood is determined by an AMH test, which is a blood test. It is a useful diagnostic tool for determining a woman’s level of fertility and for forecasting how she will react to fertility treatments. AMH testing may be advised for several reasons, including:
- Predicting the likelihood of conception while evaluating ovarian reserve
- Choosing the most effective fertility treatments
- PCOS diagnosis
- Knowing when menopause will start
- The effectiveness of ovarian suppression therapy in cancer patients is being monitored.
The test can be done at any point during the menstrual cycle because AMH levels are generally constant.
Why do I have low AMH?
Low AMH levels can be caused by several variables, some of which are listed below:
Age: Age is the most frequent cause of low AMH levels. A woman’s ovarian reserve naturally decreases as she ages, which results in lower levels of AMH. The decline quickens as menopause approaches in women.
Genetics: AMH levels may be lower even at a younger age in some women because of inherited ovarian reserve issues from their mothers.
Autoimmune disorders: Low AMH levels can be caused by autoimmune diseases that negatively affect ovarian function, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Environmental factors: Lower levels of AMH may result from adverse effects on the ovarian reserve caused by exposure to environmental toxins or chemicals.
Medical treatments: Low AMH levels can result from certain treatments that harm the ovaries and reduce the ovarian reserve, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer.
Surgical interventions: The ovarian reserve can occasionally be impacted by ovarian surgeries, such as the removal of ovarian cysts or treatment for endometriosis, and this can result in a drop in AMH levels.
If you are worried about low AMH or are having fertility problems, you must speak with a healthcare provider. They can offer a thorough assessment, taking into account every potential factor that may be affecting your fertility, and, based on your particular situation, recommend the most suitable interventions or treatments.
What Can an AMH Test Indicate?
The results of an AMH test, which indicate a woman’s ovarian reserve status, offer crucial information about her reproductive health. The following is a typical interpretation of the findings:
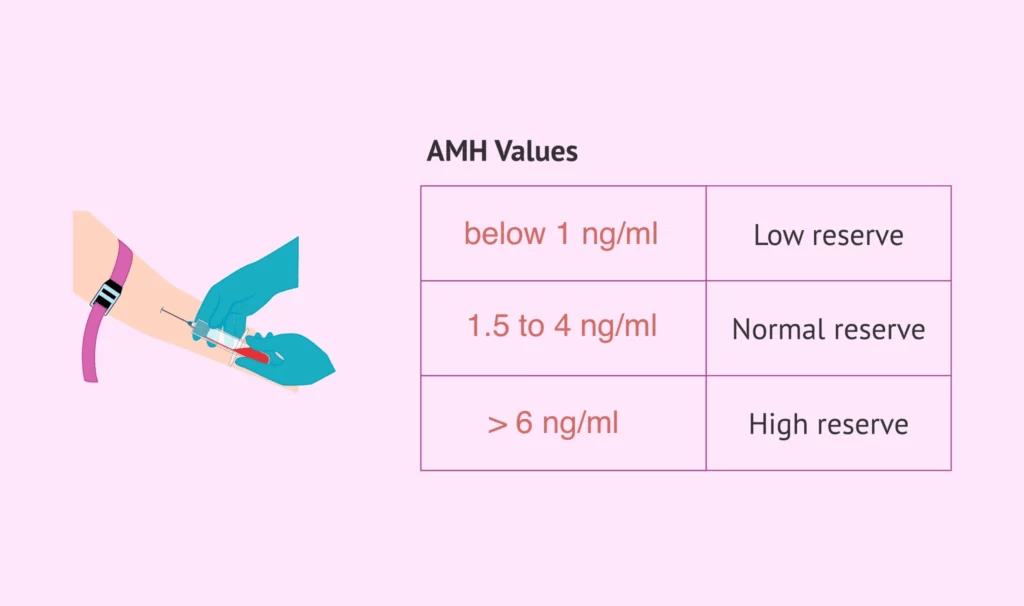
High AMH levels: AMH levels that are higher than normal may indicate a larger ovarian reserve, indicating a higher likelihood of conceiving naturally or with the aid of ARTs like in vitro fertilization (IVF). However, abnormally high AMH can also be a sign of PCOS, a hormonal disorder that can impact fertility.
Normal AMH levels: An average ovarian reserve and average chances of conceiving and responding to fertility treatments are indicated by an AMH that is normal.
Low AMH levels: AMH below normal may indicate a depleted ovarian reserve, which can make it more challenging to get pregnant and may be a sign that menopause is coming. In these situations, medical professionals might suggest aggressive fertility treatments or take other family-building options into account.
What is the AMH Test unable to indicate?
There are some restrictions on what an AMH test can reveal, despite the fact that it offers useful information about a woman’s ovarian reserve:
Egg quality: Although the test counts the eggs, it cannot assess their quality. A healthy pregnancy and chance of conception are directly related to egg quality.
Fertility potential: One aspect of fertility is AMH. Successful conception also depends on a number of other elements, including the male partner’s sperm quality, uterine health, and tubal patency.
Guarantee of conception: Both a high and low AMH does not preclude pregnancy. Successful conception is not necessarily correlated with high AMH levels. Success in conception depends on the particular circumstances of each individual and is influenced by a variety of factors.
The specific timing of menopause: AMH cannot predict the precise timing of menopause, but they can give a general indication of when a woman may enter it.
In conclusion, an AMH test is a useful tool for determining a woman’s ovarian reserve and fertility potential. To gain a thorough understanding of a woman’s reproductive health, it is crucial to take into account the test’s limitations and combine the results with other diagnostic methods and clinical assessments.
How do AMH levels affect you, and what do they mean?
The concentration of the hormone known as AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) in a woman’s blood is referred to as AMH. Granulosa cells in ovarian follicles produce the hormone AMH, which is used as a marker for ovarian reserve, or the number of viable eggs still present in the ovaries. The hormone levels can provide important clues about a woman’s potential for conception and aid in predicting how well she will respond to fertility treatments. What various AMH levels might mean for you is as follows:
Normal AMH levels: A normal AMH indicates an average ovarian reserve, which suggests an average likelihood of conception and a favorable response to fertility treatments.
High AMH levels: The probability of conceiving naturally or using assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) is generally increased when an individual’s AMH is higher than average because this indicates a larger ovarian reserve. The hormonal condition polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can affect fertility, can also be indicated by abnormally high AMH.
Low AMH levels: AMH levels that are below average may point to a depleted ovarian reserve, making it more difficult to conceive and possibly indicating that menopause is approaching. In such situations, medical professionals might suggest aggressive fertility treatments or look into alternative family-building options.
It’s important to keep in mind that AMH levels are just one aspect of fertility; other elements such as egg quality, tubal patency, uterine health, and the quality of a male partner’s sperm can also affect conception success.
What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant?
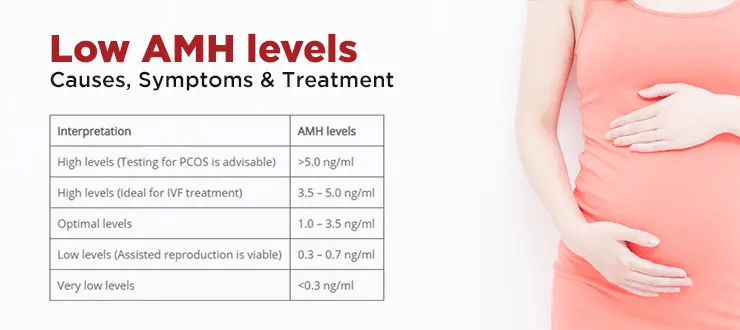
AMH levels between 1.0 and 4.0 ng/ml are considered to be a good range for getting pregnant because they signify a healthy ovarian reserve and increase the chance of naturally conceiving. AMH levels are just one aspect of fertility; other elements like egg quality, tubal patency, uterine health, and a man’s sperm quality also affect the probability of conception.
Women’s AMH levels can vary greatly, and what one person might deem to be a “good” level may not be the same for another. In general, larger ovarian reserves and improved fertility potential are linked to higher AMH. However, since fertility is influenced by a variety of factors, some of which cannot be detected through AMH testing alone, there is no particular AMH that ensures pregnancy.
Average AMH Levels (in pmol/l) for Women by Age
| Age Group | Average AMH Levels (pmol/l) |
|---|---|
| 20s | 28 – 48 |
| 30s | 15 – 28 |
| 40s | 1 – 8 |
What is a Good AMH level for IVF?
A woman’s ovarian follicles produce the hormone known as anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), which is used as a gauge of her ovarian reserve. A right ovarian reserve is a sign of a good AMH for IVF, which can raise the chance of success with the procedure.
Women’s AMH levels can vary greatly, and there is no single “good” level that applies to everyone. However, in women of reproductive age, AMH levels typically range from 1.0 to 4.0 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL), with levels above 1.0 ng/mL typically considered favorable for IVF. It is crucial to remember that AMH is just one of many variables that can affect how well IVF works; having a healthy AMH does not ensure a successful IVF procedure.
A high AMH in a woman frequently denotes that she has more eggs in reserve in her ovary. This can be helpful for IVF as it enables fertility specialists to retrieve more eggs during the egg retrieval procedure, increasing the chance of obtaining viable embryos for transfer.
On the other hand, a low AMH may indicate a reduced ovarian reserve, which can make IVF more difficult. There may be fewer eggs produced by women with low AMH during ovarian stimulation, which would reduce the number of embryos available for transfer. Lower IVF treatment success rates may result from this. But it’s important to keep in mind that every person’s fertility journey is different, and some women with low AMH can still get pregnant through IVF.
Low AMH Levels: Treatment Options
Low levels of AMH in a woman’s blood are a sign of a depleted ovarian reserve, which can make it harder to get pregnant. Low AMH levels can be treated, even though it is impossible to stop the ovarian reserve’s natural decline:
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF, a popular fertility procedure, may be successful for women with low AMH. IVF involves taking eggs out of the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a lab, and placing the resulting embryos back into the uterus. Fertility experts can increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy by carefully monitoring and managing the process.
Donor Eggs: Using donor eggs can be a viable option for women who have significantly reduced ovarian reserves to improve their chances of having a successful IVF cycle. The quality of the embryos produced through IVF can be improved by using donor eggs from younger, healthier donors, potentially increasing the pregnancy rate.
Individualized Ovarian Stimulation Protocols: In order to stimulate the ovaries in women with low AMH levels, fertility specialists can create customized ovarian stimulation protocols. By using carefully chosen medications and dosages to promote the development of mature, healthy eggs, these protocols frequently place more emphasis on improving egg quality than quantity.
Lifestyle Changes: Even for women with low AMH levels, a healthy lifestyle can support overall fertility. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and abstaining from harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol are all part of this.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): According to some studies, taking CoQ10, a natural antioxidant, may help women with low AMH levels produce eggs with higher quality.
How to Increase AMH Levels
There are some actions women can take to support their general fertility and enhance the quality of their eggs, even though it is not possible to significantly raise AMH levels or stop the ovarian reserve’s natural decline.
- Take Supplements: Women with low AMH levels may benefit from taking supplements like DHEA and Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) to enhance the quality of their eggs.
- Avoid Environmental Toxins: Fertility can be harmed by exposure to some environmental toxins, including chemicals in some plastics and cigarette smoke. Taking action to reduce exposure to these toxins can help to improve egg quality and general fertility.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote general health and fertility. Fertility can also be positively affected by regular exercise, stress reduction, and getting enough sleep.
How Can AMH Levels Improve Naturally?
- Eat a balanced diet that includes fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- For hormone regulation, engage in light exercise.
- Yoga or meditation can be used to reduce stress.
- Get adequate, restful sleep.
- Limit your alcohol intake and smoking.
- Continue to be a healthy weight.
- Reduce your exposure to dangerous chemicals.
- Be sure to hydrate yourself.
- Caffeine intake should be moderate.
- Before taking supplements, speak with a medical professional.
Also Read: What are the Common Symptoms of Blocked Fallopian Tube?
FAQs about Good AMH Levels and Pregnancy
Q. Can a low AMH level prevent pregnancy entirely?
Although a low AMH might signal a depleted ovarian reserve, pregnancy is not always impossible. Lower AMH levels do not prevent a woman from becoming pregnant; however, it may necessitate additional assistance or fertility treatments.
Q. Is it possible to increase AMH levels naturally?
While it is difficult to significantly raise AMH levels, living a healthy lifestyle, controlling stress, and getting medical help for underlying conditions can all have a positive impact on hormonal balance and possibly raise AMH levels.
Q. Are there specific AMH levels considered too high for pregnancy?
A condition known as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be indicated by extremely high AMH levels. Infertility issues and irregular menstrual cycles are common in women with PCOS.
Q. How often should I check my AMH levels?
The frequency of AMH testing is determined by the individual. Women in their late twenties and early thirties should consider regular AMH testing as part of their family planning. However, for personalized recommendations, always consult your healthcare provider.
Q. Can stress impact AMH levels?
Yes, prolonged high-stress levels have the potential to disrupt hormonal balance, including AMH levels. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and seeking emotional support is critical for overall well-being.
Q. Does a good AMH level guarantee pregnancy?
A high AMH suggests better ovarian reserve and fertility prospects, but pregnancy is not guaranteed by it. Numerous physiological aspects, such as sperm health, egg quality, and other variables all affect conception.
Conclusion
For anyone wishing to start a family, it is essential to comprehend the importance of AMH levels. There are a number of things to take into account before starting the pregnancy journey, even though a healthy AMH can improve fertility prospects. People can increase their chances of getting pregnant by living a healthy lifestyle, getting medical help when necessary, and learning about their options for fertility. Please keep in mind that everyone’s journey is different, and getting help from medical professionals and/or receiving emotional counseling can help the process go more smoothly and easily.



[…] Also Read:- What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant? […]
[…] Also Read: What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant? […]
[…] ovaries produce the hormone anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH). It is a measure of the amount of eggs still present in the ovaries, or ovarian reserve. Age and […]