Menopause and andropause are two separate stages in the life cycles of men and women, respectively. Both of these times are characterized by hormonal changes that can have a substantial impact on the body and general well-being. Understanding the differences between menopause and andropause is critical for both individuals going through these transitions and their healthcare providers. This comprehensive book will investigate the distinctive elements of menopause and andropause, including symptoms, causes, and treatment choices. By the conclusion, you’ll have a good grasp of how these hormonal shifts affect men and women differently.
Overview- Menopause and andropause
Hormonal fluctuations are a normal aspect of both men’s and women’s lives. Menopause and andropause are two different stages in which hormonal balance changes significantly. Menopause normally affects women in their late 40s or early 50s, but andropause, also known as “male menopause,” affects men in their 40s or 50s. These times are distinguished by a drop in sex hormones, most notably estrogen in women and testosterone in males.
Understanding the distinctions between menopause and andropause is critical for those going through these changes. While both menopause and andropause include hormonal changes, they present in various ways and have distinct impacts on the body. In the following parts, we will go deeper into menopause and andropause, investigating symptoms, causes, and management techniques.
Menopause: A Natural Transition in a Woman’s Life

Menopause is the period in a woman’s life when she no longer menstruates and becomes infertile. It is formally diagnosed when a woman goes 12 months without having a menstrual period. Menopause is a natural biological process that is frequently accompanied by physical and mental problems.
Symptoms of Menopause
Menopause symptoms vary significantly from woman to woman, however, the following are some of the most common:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Irregular periods
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood swings and irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Fatigue and decreased energy levels
- Weight gain
- Decreased libido
Causes of Menopause
The primary cause of menopause is the normal fall in reproductive hormones, particularly estrogen. As women age, their ovaries generate less estrogen, causing alterations in the menstrual cycle and, finally, the cessation of periods. The average age of menopause in most women is around 51 years old, however, it can occur earlier or later based on a variety of factors such as genetics and lifestyle.
Impact on Women’s Health
Menopause causes various changes in a woman’s body and can have a substantial impact on her overall health. The decrease in estrogen levels associated with menopause can increase the risk of various health issues such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and urinary incontinence. It is critical for women to take proactive measures to maintain their health before and after menopause, such as regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and frequent health check-ups.
Andropause: The Male Counterpart to Menopause

Andropause, often known as “male menopause” or “late-onset hypogonadism,” is the steady reduction in testosterone levels in males as they age. Unlike menopause, which is characterized by a rapid stop of menstruation, andropause begins gradually and may last several years. After the age of 30, testosterone levels in men are thought to fall by about 1% every year.
Symptoms of Andropause
Andropause symptoms might vary from person to person and may be similar to menopause symptoms. Among the most common symptoms are:
- Decreased libido and sexual function
- Fatigue and decreased energy levels
- Mood swings and irritability
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat, especially around the abdomen
- Difficulty concentrating and memory problems
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or sleep apnea
Causes and Contributing Factors
The normal fall in testosterone production that happens with age is the primary cause of andropause. Other circumstances, however, can contribute to the onset and severity of andropause symptoms. Poor food, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol intake, and chronic stress can all hasten the fall in testosterone levels. Obesity, diabetes, and hypothyroidism are among medical disorders that might alter hormone production and increase symptoms.
Comparing Menopause and Andropause: Similarities and Differences
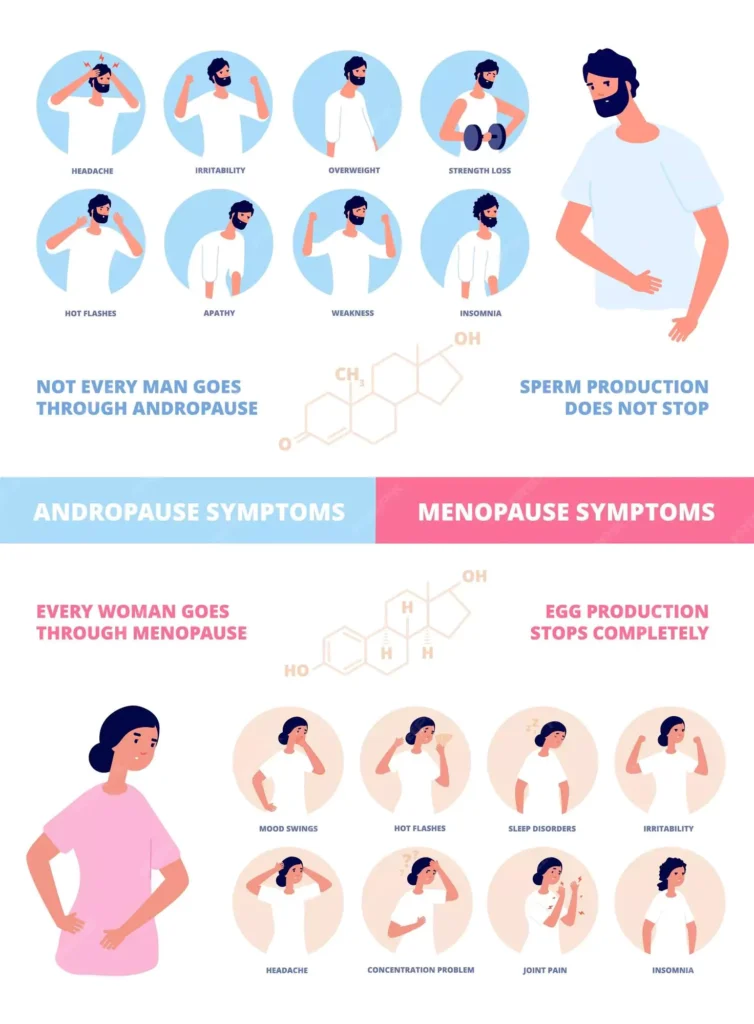
While menopause and andropause are distinct stages in the lives of women and men, they do share some symptoms and consequences on the body. However, there are some significant differences between the two. Let’s take a closer look at these parallels and differences.
Shared Symptoms
Both menopause and andropause can cause a range of similar symptoms, including:
- Fatigue and decreased energy levels
- Mood swings and irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Decreased libido and sexual function
- Memory problems and difficulty concentrating
- Weight gain and changes in body composition
Unique Symptoms in Menopause
Menopause is characterized by the cessation of menstruation and a decrease in estrogen levels. This hormonal shift might cause specific symptoms in women, such as:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse
- Urinary incontinence or increased frequency of urination
- Changes in skin elasticity and appearance
- Increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures
Unique Symptoms of Andropause
Andropause, on the other hand, is characterized primarily by a decrease in testosterone levels. This hormonal shift may contribute to the following male symptoms.:
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat, especially around the abdomen
- Loss of facial and body hair
- Enlarged breasts (gynecomastia)
- Erectile dysfunction or decreased sexual function
- Reduced sperm count and fertility
Managing Menopause and Andropause: Treatment Options
Menopause and andropause can both have a negative impact on a person’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are a variety of therapy alternatives available to alleviate symptoms and increase general well-being during these transitions.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a frequent treatment for menopausal and andropause symptoms. HRT involves replacing diminishing hormones with synthetic or bio-identical hormones in order to restore hormonal balance in the body. Estrogen replacement therapy is routinely suggested for menopausal women, but testosterone replacement therapy is frequently indicated for men experiencing andropause. It is critical to contact with a healthcare expert to identify the most appropriate form and dose of HRT based on individual needs and health state.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
In addition to pharmacological therapies, various lifestyle adjustments and self-care practices can assist in managing the symptoms of menopause and andropause. These may include:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can help improve mood, maintain muscle mass, and manage weight.
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and hormone balance.
- Stress management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, can help alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal changes.
- Adequate sleep: Getting enough restful sleep is crucial for hormonal balance and overall well-being. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a conducive sleep environment can promote better sleep quality.
- Supportive therapies: Some individuals may find relief from symptoms through complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and massage.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, in addition to traditional treatments, can help manage symptoms during menopause and andropause. Herbal supplements, homeopathy, and naturopathy are examples of these. Before implementing any alternative therapies, it is critical to consult with a qualified healthcare expert to evaluate their safety and efficacy.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider?

While menopause and andropause are natural processes, it is critical to seek professional assistance if the symptoms have a substantial impact on everyday life or if there are concerns about overall health. A healthcare provider, such as a gynecologist or urologist, can offer advice and make recommendations depending on an individual’s needs.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare practitioners play an important role in menopausal and andropause management by providing an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment programs, and continuous support. They can help with diagnosing symptoms, monitoring hormone levels, and selecting the best therapy options depending on an individual’s unique circumstances.
Diagnostic Methods and Tests
To diagnose menopause, healthcare experts may look at a woman’s medical history, physical exam, and blood testing to detect hormone levels. For andropause, healthcare providers may assess symptoms, perform a physical examination, and request blood tests to determine testosterone levels. These diagnostic techniques assist healthcare providers in developing an accurate picture of an individual’s hormonal condition and guiding treatment recommendations.
Tips for Coping with Hormonal Changes
Coping with the hormonal changes that accompany menopause and andropause can be difficult. During this transitional period, however, there are various ways that individuals can use to control symptoms and increase general well-being.
Emotional Support and Communication
Seeking emotional support from loved ones, friends, or support groups can be a lifeline during menopause and andropause. Sharing experiences, thoughts, and feelings with trusted people can help reduce stress and promote a sense of belonging. Communication with a partner or spouse about the physical and emotional changes that occur during this period can help to enhance the connection and encourage understanding.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle throughout menopause and andropause helps improve hormone balance and overall well-being. This includes the following:
- Maintaining a balanced diet: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods can support hormonal health and provide essential nutrients for optimal functioning.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can help manage weight, improve mood, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Adequate sleep: Prioritizing quality sleep can promote hormonal balance and enhance overall health and vitality.
- Stress management: Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in hobbies, can help alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal changes.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol intake can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of certain health conditions.
Stress Management Techniques

Stress can have a substantial impact on hormonal balance and increase symptoms of menopause and andropause. Implementing stress management practices can assist individuals in dealing with the problems of hormonal changes more efficiently. Among the effective stress management approaches are:
- Mindfulness meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help individuals cultivate a sense of calm and reduce stress levels.
- Deep breathing exercises: Taking slow, deep breaths can activate the body’s relaxation response and promote a sense of calm.
- Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as yoga or tai chi, can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
- Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy: Taking time for enjoyable activities can provide a much-needed break from stress and enhance emotional well-being.
Conclusion: the difference between menopause and andropause
Menopause and andropause are natural stages in women’s and men’s lives that signify significant hormonal changes. While they share certain symptoms, there are also significant distinctions between the two. Understanding these distinctions is critical for both persons going through these changes and their healthcare providers. Individuals can effectively manage symptoms and improve their general well-being during this transitional stage of life by obtaining professional support and implementing lifestyle modifications.
As with any health-related concern, it is critical to get personalized advice and guidance from a skilled healthcare expert based on specific circumstances. Individuals can navigate menopause and andropause with confidence and preserve optimal health and well-being with the correct support and management techniques in place.